by Melissa Brenes-Bastos, mbrenes@vt.edu
Demers (2009) defined Geographic Information Systems (GIS) as “a system designed to input, store, edit, retrieved, analyze, and output geographic data and information”. As all systems GIS is composed of integrated parts that allow it to perform correctly, these parts include: (1) computer hardware and software, (2) space and organization, (3) personnel and (4) data and information. (Demers, 2009)
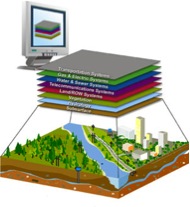
Over 25 hundred years of geographic research and investigation, result on geographic information systems evolution, the first stages of GIS were focusing on exploration unknown lands, their inhabitants and phenomena’s, in other words the primary focus was discovering. (Demers, 2009) It was explain by Demers (2009) that the need of explain phenomena’s lead researcher to create an outcome of pattern explanations for different distributions, in the early 1960’s the Department of Forestry and Rural Development of Canada pursue a project to manage the territory of Canada, this was the first big scale project. With this project the first operational system ever built was created – Canada Geographic Information Systems-, this creation lead to more research and exploring which conduce to the actual GIS, as we know now a days. (Demers, 2009)
Continue reading “RESEARCH BRIEF: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Wood Products Industry”